 When Do I Need to Use a Biocompatible Resin in Orthodontics?
When Do I Need to Use a Biocompatible Resin in Orthodontics?
Biocompatibility is required by the FDA for the manufacture of any ‘medical devices’ that will come into direct contact with the skin or oral tissue. Dental and orthodontic models that are used to fabricate clear aligners, or other appliance do not have to be printed with bio-compatible materials.
Direct printed indirect bonding trays, occlusal splints, denture bases, or other printed items that qualify as a medical devices and will come into direct contact with tissue should be printed using a bio-compatible resin.
Currently, bio-compatible resins for use in orthodontics are manufactured by FormLabs, Stratasys, and Envisiontec just to name a few suppliers.
What Does It Mean for A Resin to be Bio-compatible?
Typical 3D printed materials undergo ASTM International standards testing to evaluate material properties like tensile strength, flexural modulus, etc. However, bio-compatible materials must undergo a completely separate set of tests that are according to ISO standards, which can get expensive very quickly. These tests can cost upwards of $100,000 per resin, depending on the medical or dental indications for the resin.
There may not actually be any material difference between standard resins and bio-compatible resins from the same company; however, to produce medical devices with a resin, for the company be able to assert ‘medical claims,’ and to market directly to the dental and medical market the ISO testing is mandatory.
To be classified as a bio-compatible materials, 3D printed resins will undergo biologic evaluation according to ISO 10993-1: 2009 to address cytotoxicity, genotoxicity, and delayed hypersensitivity, and USP plastic class VI, which includes the test for irritation, acute systemic toxicity and implantation.
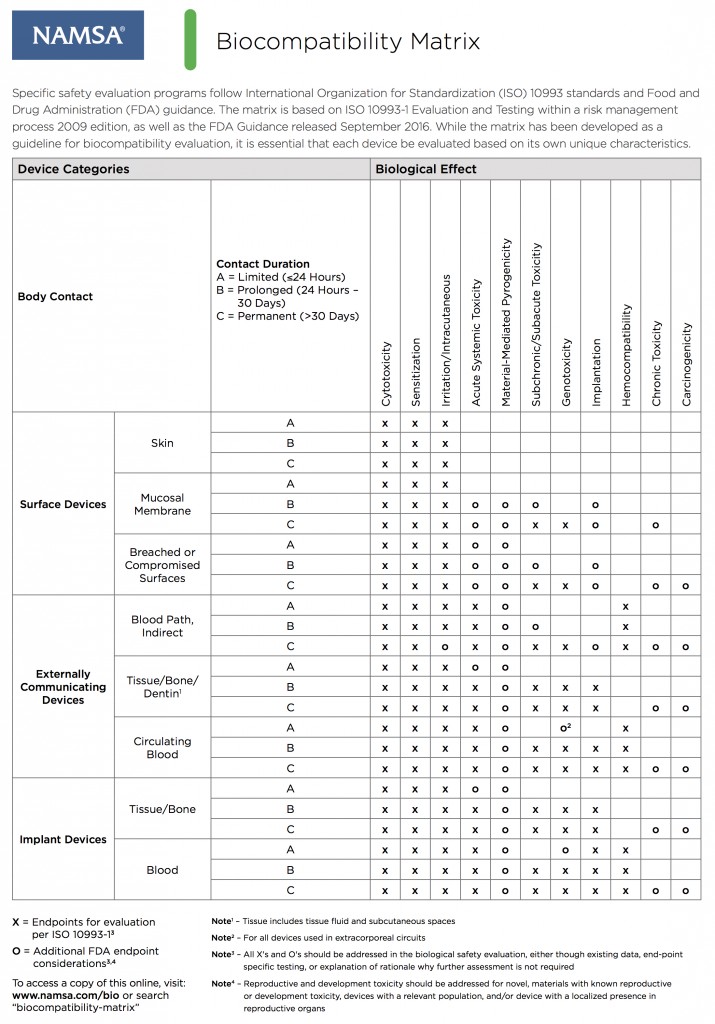 Resins may also undergo additional ISO testing for certain material properties pertinent to their intended use. For example, a bio-compatible dental resin might undergo ISO 20795-1:2013 testing, which applies to denture base polymers where the manufacturer might be making advertising claims regarding impact resistance.
Resins may also undergo additional ISO testing for certain material properties pertinent to their intended use. For example, a bio-compatible dental resin might undergo ISO 20795-1:2013 testing, which applies to denture base polymers where the manufacturer might be making advertising claims regarding impact resistance.
Leave a Reply